


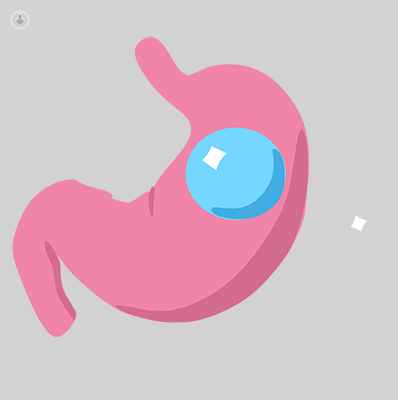
What is the gastric balloon?
A gastric balloon is a silicone device of a spherical shape that is introduced into the stomach of patients struggling with obesity. By doing so, patients do not feel the need to eat as much and feel full for longer. This can help such patients to lose weight. It is the most effective solution to fight obesity without the need for invasive surgery.
Why have a gastric balloon?
The gastric balloon is indicated for obese patients between 18 and 60 years old with a body mass index (BMI) of 30-40. The gastric balloon makes it easier for patients to maintain a diet aimed at losing weight and reducing food intake. It is important that those who choose to have a gastric band are committed to weight loss and having a healthier lifestyle for the long-term.
What does having a gastric balloon involve?
First there is an initial assessment in which the patient's clinical history is assessed, and a physical examination performed. The gastric balloon is introduced endoscopically and filled with serum to fill the balloon. By doing this, the filled balloon occupies a considerable portion of the stomach, causing a sensation of satiety in the patient and, as a result, the patient feels less hungry and fuller for longer after eating.
Preparation for the gastric balloon:
Before placing the gastric balloon, a post-procedure diet will be discussed with the specialist, as well as advice given on exercise. Before the balloon is inserted, the patient must fast for 6-12 hours.
Aftercare:
You can consume some liquids a few hours after the procedure. During the first few days of adaptation of the gastric balloon, a transition is made from a liquid diet to a solid diet, which is adjusted to each patient and situation. The balloon is usually removed six months after insertion and it is removed using an endoscope. Once withdrawn, the patient continues undergoing a multidisciplinary medical follow-up to consolidate the healthy dietary habits.