


What is a premature baby?
Premature or preterm babies are babies who are born before week 37 of pregnancy (the normal duration of gestation is around 40 weeks). Premature babies are generally weaker and statistically suffer from more complications during their first weeks of life.
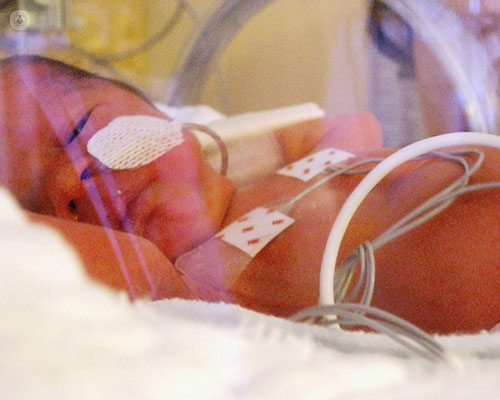
What are the symptoms experienced by a premature baby?
The main sign of a baby being premature is their weight being below average, even though being underweight is not always a sign of a premature baby. There are three different categories of preterm babies, divided by underweight severity: 1.50 to 2kg, less than 1.5kg and less than 1kg.
What causes a premature birth?
Premature birth can be caused by several factors. On the mother’s side, it can occur as a consequence of cardiopathies, infections, pre-eclampsia, anaemia, uterine or placental abnormalities or an unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking illegal drugs). Other factors include multiple pregnancies, chorioamniotic membrane separation, chromosomal abnormalities and altered foetal development (due to the placenta not ensuring an adequate nutrients and oxygen supply to the foetus).
How are premature babies treated and cared for?
Preterm and underweight babies are kept in an incubator, a machine that simulates the temperature, oxygenation and nutrients supply of the mother’s uterus. Once the baby has reached the same size and development stage as those of a regular term pregnancy, the incubator will no longer be necessary. However, during the first two years of the baby’s life, the parents will need to give him or her extra care, due to an increased risk of breathing problems (caused by the artificially induced lung development).
Which doctor should I talk to?
You have to see an obstetrician and gynaecologist to adequately treat a premature new-born.