


What are pectoral implants?
Pectoral implants are a relatively recent development in the world of plastic surgery but have become more popular over the years. Pectoral implants are inserted into the chest area in order to give shape and/or size (i.e thickness, or fullness). Unlike implants traditionally used in breast surgery and augmentation, pectoral implants are typically made from a solid yet supple material which comes in different sizes and can be tailored to the individual and their needs.
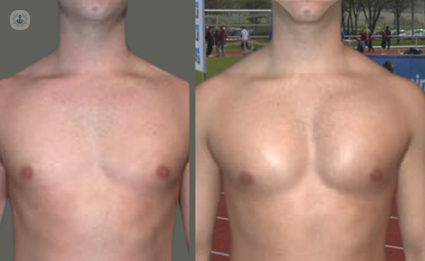
Why is the procedure done?
In some cases, it can be difficult for men to achieve the pectoral definition and size they desire no matter how much they exercise and how they change their diet. In some individuals, there is also a noticeable difference in size between the sides of the chest, and pectoral implants can rectify this difference. The individual may also have experienced an injury or illness which affects the chest and the pectorals, and therefore looks to surgery in order to correct the change.
What does it involve?
Before the procedure, the plastic surgeon will discuss your needs and you will decide on the size and shape of the implant together. In order for implants to be inserted, the patient is first put under general anaesthetic or sedated. Incisions are typically made under the armpits, meaning scarring is less visible, and the implants are inserted under the existing muscles.
In some cases, some decide to combine the procedure with other aesthetic procedures, such as lipostructure, liposculpture, or fat transfer.
How do you prepare for pectoral implants?
Before the procedure you will speak to your surgeon to decide on whether it is the right choice for you, and what you wish to achieve through surgery. When meeting your surgeon, you will also have to give information on your medical history, whether you have had any previous operations, and if you have any pre-existing conditions. Your surgeon will also discuss any risks the procedure entails and how it is carried out, and you can ask them any questions you need to.
Before the procedure is carried out, you will need to do a blood test to check your red and white blood cell counts. Before the operation, you must not eat, drink, or smoke for at least 6 hours. Your surgeon will also advise you of medication you must not take beforehand, such as aspirin.
Aftercare
After the procedure has been carried out, you will typically be kept overnight at the clinic or at the hospital. After you have been discharged, you will need to wear a support vest or bandage which helps to reduce swelling. You may experience some pain for about a week or so after the procedure, or feel sore and tender. During the recovery period, it is important to rest, drink enough water (keep hydrated) and not strain or overexert yourself. You will need to be off work for at least 1-2 weeks.
After the procedure you will not be able to do sport or engage in heavy lifting for 6 weeks. During the weeks following the procedure, you can take painkillers to help reduce the pain and discomfort. Your surgeon will put a follow-up consultation plan in place with you to check on your progress after the procedure and see how your body is healing. Swelling typically lasts for a few weeks after the initial procedure, so it is difficult to gauge results immediately. As the swelling goes down, you will be able to see what your new implants look like.
Alternatives
Fat transfer can be used to augment the chest, but it is worth noting that only a certain amount of fat can be transferred and injected. Fat transfer may also require further procedures, and does not feel exactly the same as implants, which are designed to replicate muscle.