


What are malformations of the nervous system?
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that covers the entire body. It is responsible for transmitting information between the brain and spinal cord and the various parts of the body through the nerves, allowing the person to feel and react to stimuli.
The nervous system is composed of:
- The central nervous system – the brain and spinal cord
- The peripheral system – the somatic system, which controls voluntary actions and the autonomic system, which controls involuntary actions.
Most are neural tube defects, i.e. birth defects in the brain, spinal cord and spine. These occur in the first month of pregnancy, before a woman knows her condition.
The most serious abnormalities are:
- Spina bifida
- Anencephaly: a large part of the brain and skull do not develop. Babies with this condition are usually stillborn or die soon after birth.
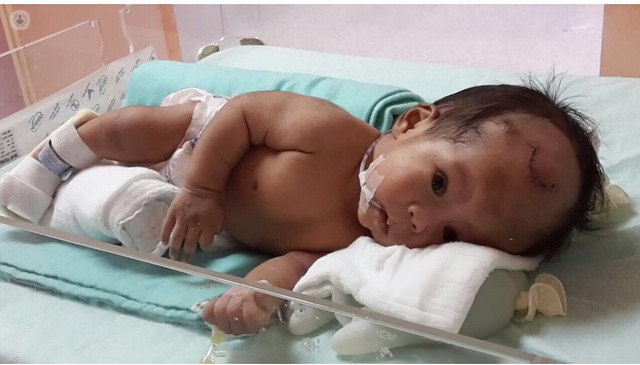
- Encephalocele: the tube does not close near the brain, with an opening in the skull forming a bulge.
- Iniencephaly: there is an extreme deformity of the spine, the baby has no neck, and the face is attached to the chest.
- Chiari malformations: part of the brain tissue passes into the spinal cord.
Prognosis of nervous system malformations
Malformations of the nervous system are serious conditions, since they can cause paralysis and disability. There are some nervous system malformations, such as inicincephaly or anencephaly in which the baby is stillborn or dies shortly after birth.
Symptoms of nervous system malformations
Some nervous system malformations have hardly any symptoms; others cause symptoms that severely impact the patient’s life, such as paralysis, physical deformities, and problems with some of the body’s systems (e.g. urinary and digestive).
Spina bifida is the most common type of nervous system malformation. It occurs when the neural tube is not completely closed. This condition causes paralysis of the legs, which can affect their motor functions for life or even cause intestinal and urinary dysfunctions. Children with spina bifida may also have intellectual disabilities. In some forms of spina bifida, there may be a lump on the back formed by a cyst coming out of the spine.
Medical tests for nervous system malformations
Imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMR) allow doctors to examine the nervous system structures.
What causes malformations of the nervous system?
Although much research has been done on the origin of nervous system abnormalities, the exact causes of why the foetal nervous system does not develop fully are unknown. It is thought that a combination of genetic, nutritional and environmental factors may cause these conditions.
It is thought that the following are potential risk factors:
- The mother is obese
- The mother has diabetes and for some reason the disease is not being well controlled
- The mother is taking certain medication to prevent seizures
- Exposure to radiation during pregnancy
Can malformations of the nervous system be prevented?
In women of childbearing age, folic acid is very important. Folic acid is a B vitamin that mainly helps the body in the creation of new cells. In fact, getting enough folic acid before and during pregnancy can help to prevent major birth defects in both the baby's brain and spine.
Folic acid can be found in the following foods:
- Green leafy vegetables
- Fruit
- Peas, nuts and peas
- Fortified breads and cereals
If the necessary amount of folic acid cannot be ingested through food, it can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Treatments for malformations of the nervous system
Encephaloceles can sometimes be treated with surgery by inserting the bulging tissue back into the skull, while correcting malformations of both the face and skull.
Treatment for spine bifida varies depending on the disease and its complications.
- Open spina bifida – with the spinal cord exposed, the opening may close before birth or within a few days of birth
- Hydrocephalus – if a baby with spine bifida has hydrocephalus, the fluid can be drained through a valve. treating hydrocephalus can prevent vision problems and blindness.
- Tied spinal cord – the cord can be separated from the surrounding tissues
- Urinary and bowel incontinence and infections – affected by myelomeningocele, the patient has nerve damage that prevents complete emptying of the bladder. It can be resolved by inserting a catheter into the bladder.
Which specialist treats malformations of the nervous system?
There are several specialists who can diagnose and treat malformations of the nervous system.
Most are dealt with by neurosurgeons, but certain conditions may warrant the involvement of a medical oncologist or neuroradiologist.