


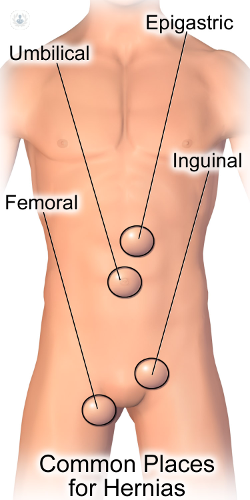
What is a femoral hernia?
A femoral hernia is fairly uncommon and is most commonly found in women. Femoral hernias are found in the groin region and can appear as a painful lump on the inner, upper thigh. The lump can be pushed back in and can sometimes become more prominent when straining or coughing. It is estimated that only 1 in 20 groin hernias are femoral hernias, and are mostly inguinal hernias. They are more common in women because women have a wider pelvis.
What are the symptoms of a femoral hernia?
Some people with a femoral hernia do not notice any bulge, lump or pain, however, larger femoral hernias produce a visible bulge in your upper thigh which can be painful, especially when straining.
What causes a femoral hernia?
A femoral hernia is the result of fatty tissue or a section of the bowel protruding through into the groin on the top of your inner thigh. The section where the protrusion can occur is called the femoral canal and is considered a weak spot in the abdominal wall muscles. The actual causes of a femoral hernia are:
What is the treatment for a femoral hernia?
Unlike other types of hernia, femoral hernias usually require treatment straight away due to potential complications associated with them. Surgery can be performed to put the bulge back into place and to fix the weakened abdominal wall. Complications that can result from femoral hernias include:
Obstruction where part of the bowel can become stuck in the femoral canal resulting in nausea and pain. Strangulation where the stuck section of bowel has its blood supply cut off (ischaemia), which required immediate surgical attention so that blood supply is restored and the tissue doesn’t die.
Surgery for treating femoral hernias can either be open surgery, or it can be performed laparoscopically. Patients can usually return home either the same day or the following day.