


What is a cardio check-up?
A cardio check-up, or cardiac screening, is designed to assess the health of the cardiovascular system, before symptoms of cardiovascular disease present. By screening for early indications, disease can be prevented or treated.
What does a cardio check-up involve?
The most common tests carried out in a cardio check-up include:
- Cholesterol test – high levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) can lead to a build-up of cholesterol in the arteries, leading to coronary artery disease.
- Blood test – to check for blood glucose levels, and certain proteins which can indicate inflammation in the body.
- Blood pressure test – both at rest, and when the heart is beating harder.
If the above tests are indicative of risk factors, further tests may be carried out, including:
- Coronary CT angiography – a CT scanner and contrast material create images of the coronary arteries to assess for any plaque or blockages.
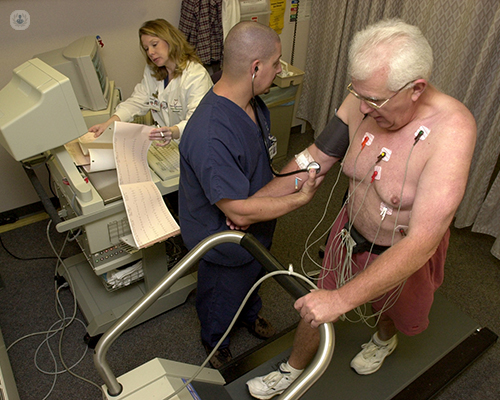
- Electrocardiography (ECG) – this measures heart activity, including heart rate and rhythm.
- Cardiac stress test – whilst walking on a treadmill or exercise bike, your heart rate, rhythm and blood pressure are measured as intensity is increased. This determines whether the heart is receiving enough blood when stressed.
- Coronary catheter angiography – pictures of the blood flowing through the coronary arteries are taken to detect narrowing or blockages.
Why is a cardio check-up done?
A cardio check-up can assess the health of the heart of someone who isn’t experiencing any symptoms. This way, signs of coronary disease can be detected early and reduce the chances of a sudden cardiac event. Early detection can allow for treatment and lifestyle changes to be made.
The following risk factors also increase the risk of people developing cardiac problems. These risk factors include:
- A family history of heart disease
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Older age
What do abnormal results mean?
If coronary artery disease is detected, there are numerous measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of heart attack. These include lifestyle measures (exercise, smoking cessation and a healthy diet), and medications to lower cholesterol and blood pressure.